Menstrual Problems
Dys – Painful; meno – Month; rrhea – Flow
Dysmenorrhea
Painful Periods/ Menstrual Cramps
- You’ll feel these cramps in your lower belly or back from mild to severe.
- They usually happen for the 1st time a year or two after a girl first gets her period.
- With age, they usually become less painful and may stop entirely after you have your first baby.
- Your doctor may call your cramps “dysmenorrheal.”
- In general Dysmenorrhea refers to pain occurring before or during menstruation or both.
Fast Facts
- It is one of the most common gynecologic complaints in young women with prevalence of 90%
- 72 % of women complaints of painful periods most commonly during the 1st day of menses. 60% of the women reports at least 1 episode of severe pain
Types of Dysmenorrhea
Primary Dysmenorrhea
- Caused by excessive levels of natural chemical prostaglandins which are made in the lining of the uterus.
- Prostaglandins prevent blood loss by promoting blood clot.
- It is believed that the presence of these chemicals narrows blood vessels in the muscles of the uterus and the intestines causing the parts to contract
Secondary Dysmenorrhea
- Caused by disorders in the female reproductive organs.
- Pain begins earlier in the menstrual cycle and also lasts longer than most period pains and cramps.
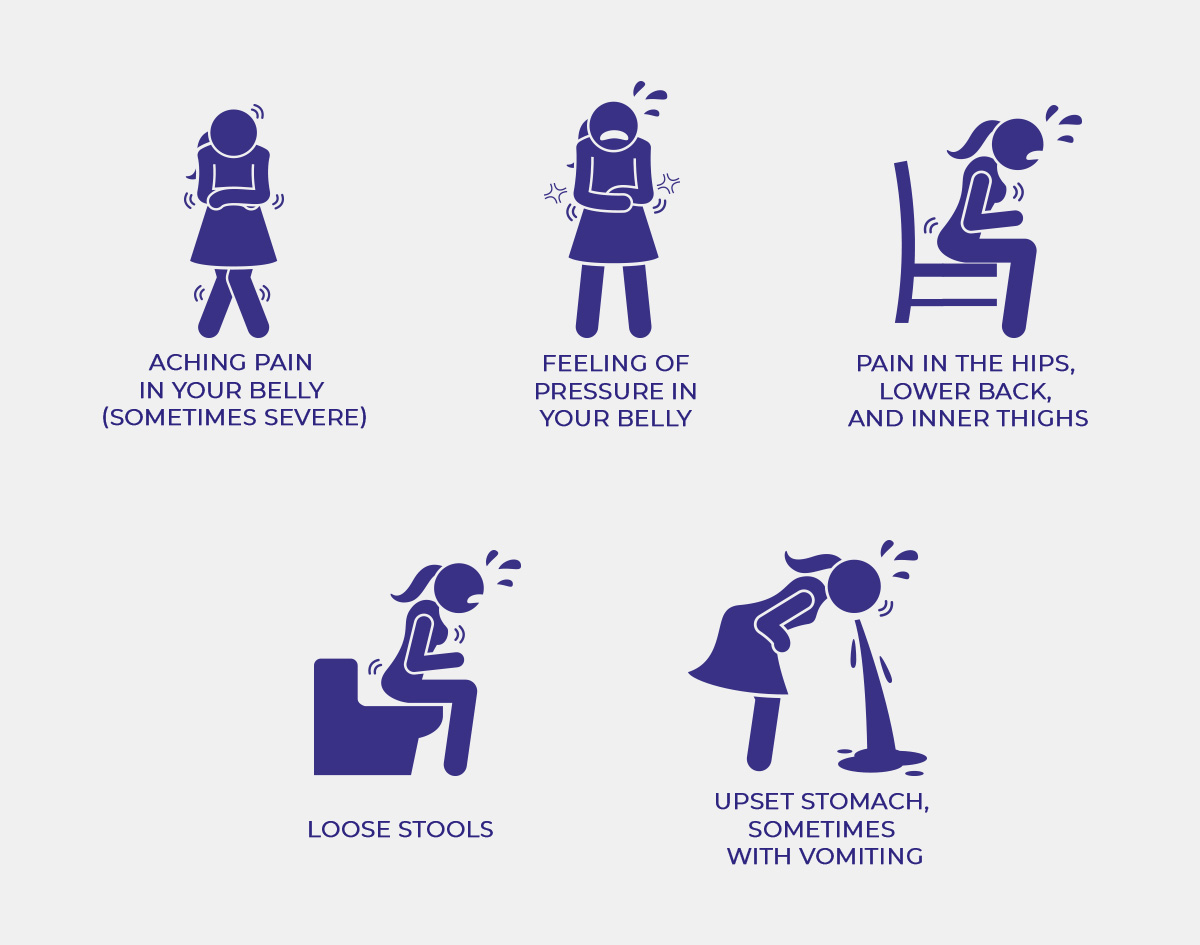
Symptoms of Dysmenorrhea
Chances are, you know all too well how it feels. You may have:
- Aching pain in your belly (sometimes severe)
- Feeling of pressure in your belly
- Pain in the hips, lower back, and inner thighs
When cramps are severe, symptoms may include:
- Upset stomach, sometimes with vomiting
- Loose stools
Take care of yourself in Dysmenorrhea
Non-medical therapies that have been recommended to relieve pain include:
- Regular exercise
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol;
- Recommend relaxation techniques such as yoga;
- Avoid exposure to extreme cold;
- Place a hot water bottle over the painful area and curl the knees onto the chest.
The management with medical and surgical interventions depends on the severity of pain and impact on daily activities.
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
- A gynecological condition marked by heavy ,excessive menstrual bleeding (which may include clots of blood) or extended menstrual bleeding
- AUB dramatically affects women’s lives, yet women wait years to seek treatment.
DID You know ?
More than 80% of women with AUB find that their heavy period is disruptive to their mental, emotional and physical well-being
AUB Symptoms
- Bleeding or spotting between periods
- Bleeding or spotting after sex
- Heavy bleeding during your period
- Menstrual cycles that are longer than 38 days or shorter than 24 days
- “Irregular” periods in which cycle length varies by more than 7–9 days
- Bleeding after menopause
AUB Treatment
- A drug to control the bleeding
- If bleeding continues, a procedure to control the bleeding
- If abnormal cells are present, high doses of a progestin or progesterone or, in postmenopausal women, sometimes removal of the uterus
Treatment of abnormal uterine bleeding depends on
- How old the woman is
- How heavy the bleeding is
- Whether the uterine lining is thickened
- Whether the woman wishes to become pregnant
Treatment focuses on controlling the bleeding and, if needed, preventing endometrial cancer.
For more information consult your Doctor.
Vaginal Atrophy

Atrophic vaginitis means the walls of your vagina have become thin drying and inflammation of the vaginal walls

This happens when your body makes too little of the hormone estrogen.

Menopause or surgical removal of the ovaries are the most common causes for a drop in estrogen.

Breastfeeding can also cause the hormone level to drop.
For many women, vaginal atrophy not only makes intercourse painful but also leads to distressing urinary symptoms
Up to 40 % of postmenopausal women have symptoms of atrophic vaginitis
Only 20 to 25 percent of symptomatic women seek medical attention
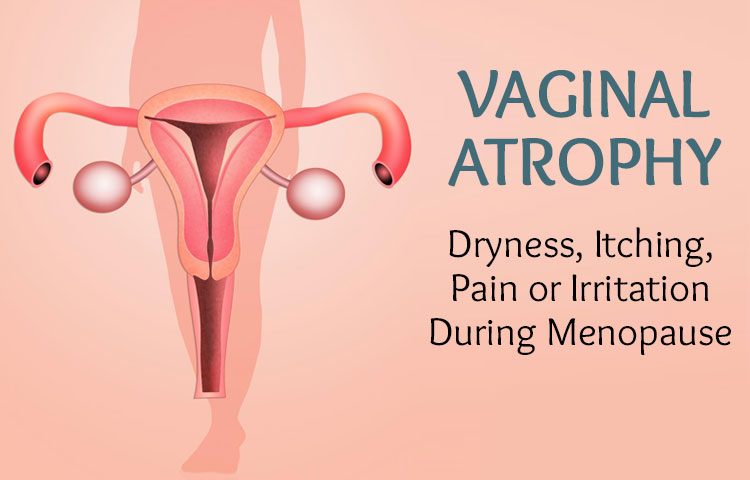
Symptoms of Atrophic Vaginitis
- Dryness due to decreased vaginal secretion
- Soreness, burning, or itching in the vagina ,chafing or other discomfort.
- Vaginal discharge
- Sex can be uncomfortable, even painful. After sex, you may have bleeding from your vagina. You may also have burning or pain when you urinate.
When to seek medical advice
- Call your health care provider right away if any of these occur:
- Fever of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher, or as directed by your healthcare provider
- Symptoms don’t go away or get worse even with treatment
- Vaginal area swells or becomes painful
- Vaginal area bleeds, but not because of your period
- Bad-smelling discharge from the vagina
- Pain or burning when you urinate or you have trouble passing urine
- Open sores develop around vagina
- The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists; Obstet Gynecol. 2013;121(4):891-896
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Heavy menstrual bleeding.https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/blooddisorders/women/menorrhagia.html Accessed July 05, 2017
- Hologic, Inc. Data on File; AUB Patient Journey Research, conducted January 2017. Survey of 1,003 women who self-identified as currently or recently experiencing heavy bleeding with need to change feminine hygiene product every hour or more; Adapted from Hoogic AUB Patient journey research; cited on 9th Sep 2019
- https://www.acog.org/Patients/FAQs/Abnormal-Uterine-Bleeding https://www.acog.org/Patients/FAQs/Abnormal-Uterine-Bleeding;Adapted from The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists;Cited on 9th Sep 2019
- https://www.acog.org/Patients/FAQs/Dysmenorrhea-Painful-Periods Adapted from The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists ;Cited on 7th Sep 2019
- Jamieson DJ, Steege JF. The prevalence of dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia, pelvic pain, and irritable bowel syndrome in primary care practices. Obstet Gynecol. 1996;87:55–8
- Harlow SD, Park M. A longitudinal study of risk factors for the occurrence, duration and severity of menstrual cramps in a cohort of college women. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1996;103:1134–42 [Published erratum in Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1997;104:386]
- Am Fam Physician. 2000 May 15;61(10):3090-3096.